- Published on

AI PROJECT-1.2 Download Dataset in JupyterLab or Jupyter Notebook
- Authors

- Name
- KAUSTUBH SHARMA
How to Download DataSet in Jupyter or JupyterLab?
STEP-0: (ONLY IF YOU ARE NOT USING SAGEMAKER NOTEBOOK INSTANCES, For SageMaker Notebook Instances user, proceed with Step-2)
- As we already using SageMaker Notebook Instance, So we don't need to install conda and other library package.
- But if we are working on a system which doesn't have Conda installed, you can install conda by Downloading from Here.
- Then to download datset, we require SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations) library, a popular tool for interpreting the output of machine learning models, which we can install using Conda using below code:
%conda install -c conda-forge shap
- If you're using JupyterLab, you have to manually refresh Jupyter kernel after the installation and updates have completed. Run the following IPython script to shut down the kernel (the kernel will restart automatically):
import IPython
IPython.Application.instance().kernel.do_shutdown(True)
STEP-1: Update Conda Version
- First, we will check current conda version using:
conda -V
- First we will update conda using below code:
conda update -n base -c conda-forge conda
- Then, again we will check current(updated) conda version using:
conda -V
STEP-2: Import SHAP Library
- First we need to import the SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations) library using below commands.
import shap #Import the SHAP library, a popular tool for interpreting the output of machine learning models.
STEP-3: Load DataSet
- Then, we have to load the Adult Census dataset (available here), also known as "Census Income" dataset to your notebook instance.
import shap # Import the SHAP library, a popular tool for interpreting the output of machine learning models.
X = shap.datasets.adult() #Load the Adult Census dataset using shap library
X #Displays the value of X
Output:
( Age Workclass Education-Num Marital Status Occupation \
0 39.0 7 13.0 4 1
1 50.0 6 13.0 2 4
2 38.0 4 9.0 0 6
3 53.0 4 7.0 2 6
4 28.0 4 13.0 2 10
... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 27.0 4 12.0 2 13
32557 40.0 4 9.0 2 7
32558 58.0 4 9.0 6 1
32559 22.0 4 9.0 4 1
32560 52.0 5 9.0 2 4
Relationship Race Sex Capital Gain Capital Loss Hours per week \
0 0 4 1 2174.0 0.0 40.0
1 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 13.0
2 0 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0
3 4 2 1 0.0 0.0 40.0
4 5 2 0 0.0 0.0 40.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 5 4 0 0.0 0.0 38.0
32557 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0
32558 1 4 0 0.0 0.0 40.0
32559 3 4 1 0.0 0.0 20.0
32560 5 4 0 15024.0 0.0 40.0
Country
0 39
1 39
2 39
3 39
4 5
... ...
32556 39
32557 39
32558 39
32559 39
32560 39
[32561 rows x 12 columns],
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, True]))
- Jupyter Notebooks retain memory throughout the notebook.So, if I put X in the next cell like below, it will show the value of X.
X
Output:
( Age Workclass Education-Num Marital Status Occupation \
0 39.0 7 13.0 4 1
1 50.0 6 13.0 2 4
2 38.0 4 9.0 0 6
3 53.0 4 7.0 2 6
4 28.0 4 13.0 2 10
... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 27.0 4 12.0 2 13
32557 40.0 4 9.0 2 7
32558 58.0 4 9.0 6 1
32559 22.0 4 9.0 4 1
32560 52.0 5 9.0 2 4
Relationship Race Sex Capital Gain Capital Loss Hours per week \
0 0 4 1 2174.0 0.0 40.0
1 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 13.0
2 0 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0
3 4 2 1 0.0 0.0 40.0
4 5 2 0 0.0 0.0 40.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 5 4 0 0.0 0.0 38.0
32557 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0
32558 1 4 0 0.0 0.0 40.0
32559 3 4 1 0.0 0.0 20.0
32560 5 4 0 15024.0 0.0 40.0
Country
0 39
1 39
2 39
3 39
4 5
... ...
32556 39
32557 39
32558 39
32559 39
32560 39
[32561 rows x 12 columns],
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, True]))
STEP-4: Disaplaying Features and Labels
- We can see that X displays features(Age, Occupation, etc.) and labels(If Person's income exceeds $50K/yr, in form of 'True' or 'False').
- So, we need to seperate them using below code.
X, Y = shap.datasets.adult() #Load the Adult Census dataset using shap library, where features are assigned to X and labels to Y
X
Y
Output:
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, True])
- As we can see from above code, only results of Y is displayed.
- But if you load individual value of X, it will show output.
X
Output:
Age Workclass Education-Num Marital Status Occupation Relationship Race Sex Capital Gain Capital Loss Hours per week Country
0 39.0 7 13.0 4 1 0 4 1 2174.0 0.0 40.0 39
1 50.0 6 13.0 2 4 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 13.0 39
2 38.0 4 9.0 0 6 0 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
3 53.0 4 7.0 2 6 4 2 1 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
4 28.0 4 13.0 2 10 5 2 0 0.0 0.0 40.0 5
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 27.0 4 12.0 2 13 5 4 0 0.0 0.0 38.0 39
32557 40.0 4 9.0 2 7 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
32558 58.0 4 9.0 6 1 1 4 0 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
32559 22.0 4 9.0 4 1 3 4 1 0.0 0.0 20.0 39
32560 52.0 5 9.0 2 4 5 4 0 15024.0 0.0 40.0 39
32561 rows × 12 columns
- And value of Y also will be displayed.
Y
Output:
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, True])
- This tells us that Cells only displays result of last variable.
- And, to display results of results of variables other than last, we have to modify code as below:
display(X) #Displays the value of X
Y #Displays the value of Y
Output:
Age Workclass Education-Num Marital Status Occupation Relationship Race Sex Capital Gain Capital Loss Hours per week Country
0 39.0 7 13.0 4 1 0 4 1 2174.0 0.0 40.0 39
1 50.0 6 13.0 2 4 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 13.0 39
2 38.0 4 9.0 0 6 0 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
3 53.0 4 7.0 2 6 4 2 1 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
4 28.0 4 13.0 2 10 5 2 0 0.0 0.0 40.0 5
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 27.0 4 12.0 2 13 5 4 0 0.0 0.0 38.0 39
32557 40.0 4 9.0 2 7 4 4 1 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
32558 58.0 4 9.0 6 1 1 4 0 0.0 0.0 40.0 39
32559 22.0 4 9.0 4 1 3 4 1 0.0 0.0 20.0 39
32560 52.0 5 9.0 2 4 5 4 0 15024.0 0.0 40.0 39
32561 rows × 12 columns
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, True])
STEP-5: Performing Some Operations with Loaded Dataset
- We can also perform certain functions here, just like if I want to display only features:
features = list(X.columns) #List all features,which is in Header Column of X
features #Display all features
Output:
['Age',
'Workclass',
'Education-Num',
'Marital Status',
'Occupation',
'Relationship',
'Race',
'Sex',
'Capital Gain',
'Capital Loss',
'Hours per week',
'Country']
- Load a version of the dataset specifically designed for display purposes.
X_display, Y_display = shap.datasets.adult(display=True) #Load Display version of Dataset
display(X_display) #Show Features of Display version of Dataset
Y_display #Show Labels of Display version of Dataset
Output:
Age Workclass Education-Num Marital Status Occupation Relationship Race Sex Capital Gain Capital Loss Hours per week Country
0 39.0 State-gov 13.0 Never-married Adm-clerical Not-in-family White Male 2174.0 0.0 40.0 United-States
1 50.0 Self-emp-not-inc 13.0 Married-civ-spouse Exec-managerial Husband White Male 0.0 0.0 13.0 United-States
2 38.0 Private 9.0 Divorced Handlers-cleaners Not-in-family White Male 0.0 0.0 40.0 United-States
3 53.0 Private 7.0 Married-civ-spouse Handlers-cleaners Husband Black Male 0.0 0.0 40.0 United-States
4 28.0 Private 13.0 Married-civ-spouse Prof-specialty Wife Black Female 0.0 0.0 40.0 Cuba
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
32556 27.0 Private 12.0 Married-civ-spouse Tech-support Wife White Female 0.0 0.0 38.0 United-States
32557 40.0 Private 9.0 Married-civ-spouse Machine-op-inspct Husband White Male 0.0 0.0 40.0 United-States
32558 58.0 Private 9.0 Widowed Adm-clerical Unmarried White Female 0.0 0.0 40.0 United-States
32559 22.0 Private 9.0 Never-married Adm-clerical Own-child White Male 0.0 0.0 20.0 United-States
32560 52.0 Self-emp-inc 9.0 Married-civ-spouse Exec-managerial Wife White Female 15024.0 0.0 40.0 United-States
32561 rows × 12 columns
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, True])
- You can see in Display version of dataset; Country, Occupation, Relationship etc. are not displayed in numeric form, instead it is displayed in Text form.
- That's why display form of dataset is used for Human Understanding purposes.
- But for models, numeric values is easier to understand or learn. That's why for overview purpose, we will use simple version, which has numeric features.
STEP-6: Displaying statistical overview of the dataset
- To display statistical overview of the dataset, we require numeric features, which are available through normal version, not with display version.
display(X.describe()) #Display statistical overview of the dataset
- Above command will display general statistical calculations like count, mean, min, max , etc.
- Output is shown below:
Age Workclass Education-Num Marital Status Occupation Relationship Race Sex Capital Gain Capital Loss Hours per week Country
count 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000 32561.000000
mean 38.581646 3.868892 10.080679 2.611836 6.572740 2.494518 3.665858 0.669205 1077.648804 87.303833 40.437454 36.718866
std 13.640442 1.455960 2.572562 1.506222 4.228857 1.758232 0.848806 0.470506 7385.911621 403.014771 12.347933 7.823782
min 17.000000 0.000000 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.000000 0.000000
25% 28.000000 4.000000 9.000000 2.000000 3.000000 0.000000 4.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 40.000000 39.000000
50% 37.000000 4.000000 10.000000 2.000000 7.000000 3.000000 4.000000 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 40.000000 39.000000
75% 48.000000 4.000000 12.000000 4.000000 10.000000 4.000000 4.000000 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 45.000000 39.000000
max 90.000000 8.000000 16.000000 6.000000 14.000000 5.000000 4.000000 1.000000 99999.000000 4356.000000 99.000000 41.000000
STEP-7: Displaying histograms of the numeric features of the dataset
What is Histogram?
- A histogram is a representation of the distribution of data.
hist = X.hist()
Output:
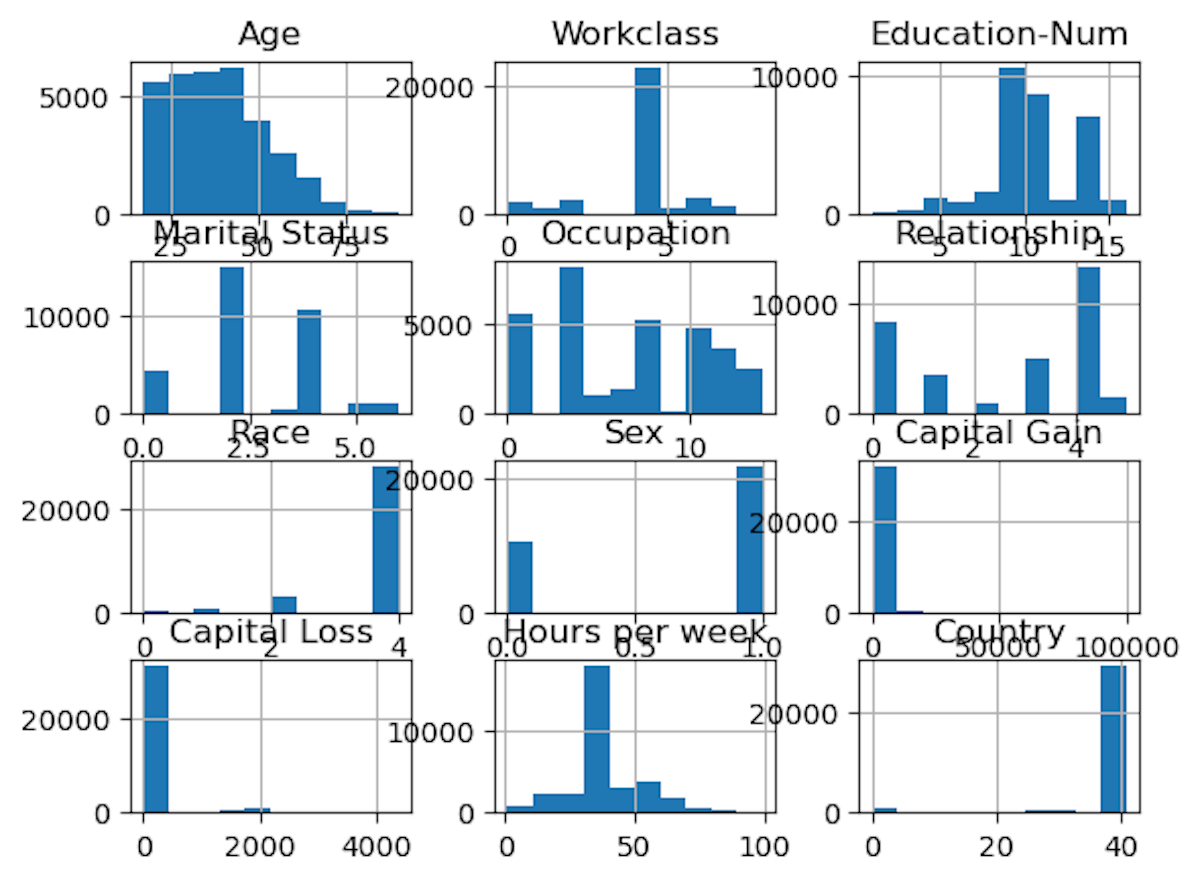
But as we can see it is not very well aligned and presentable.
- So, we have to add some parameters like bin, figsize and sharey. Let's discuss them one by one.
What is figsize in Histogram?
- Sets the size of the overall figure in inches.
- The figure size is specified as a tuple with width and height.
hist = X.hist(figsize=(10, 10))
- In this case, the width is set to 10 inches, and the height is set to 10 inches. But, still there is some space left in width, So, we can adjust accordingly.
- Let me try with 20 inch width.
hist = X.hist(figsize=(20, 10))
- This looks good. But, still I see bins are very less.
What is Bin In Histogram?
- Refers to an interval or range into which the data is divided.
- The data points are then counted or aggregated within each bin to create a visual representation of the distribution of the data.
- Default Value: 10
- I tried with multiple values, I found it, 30 seems to be gives a good histogram.
hist = X.hist(figsize=(20, 10), bins=30)
Output:
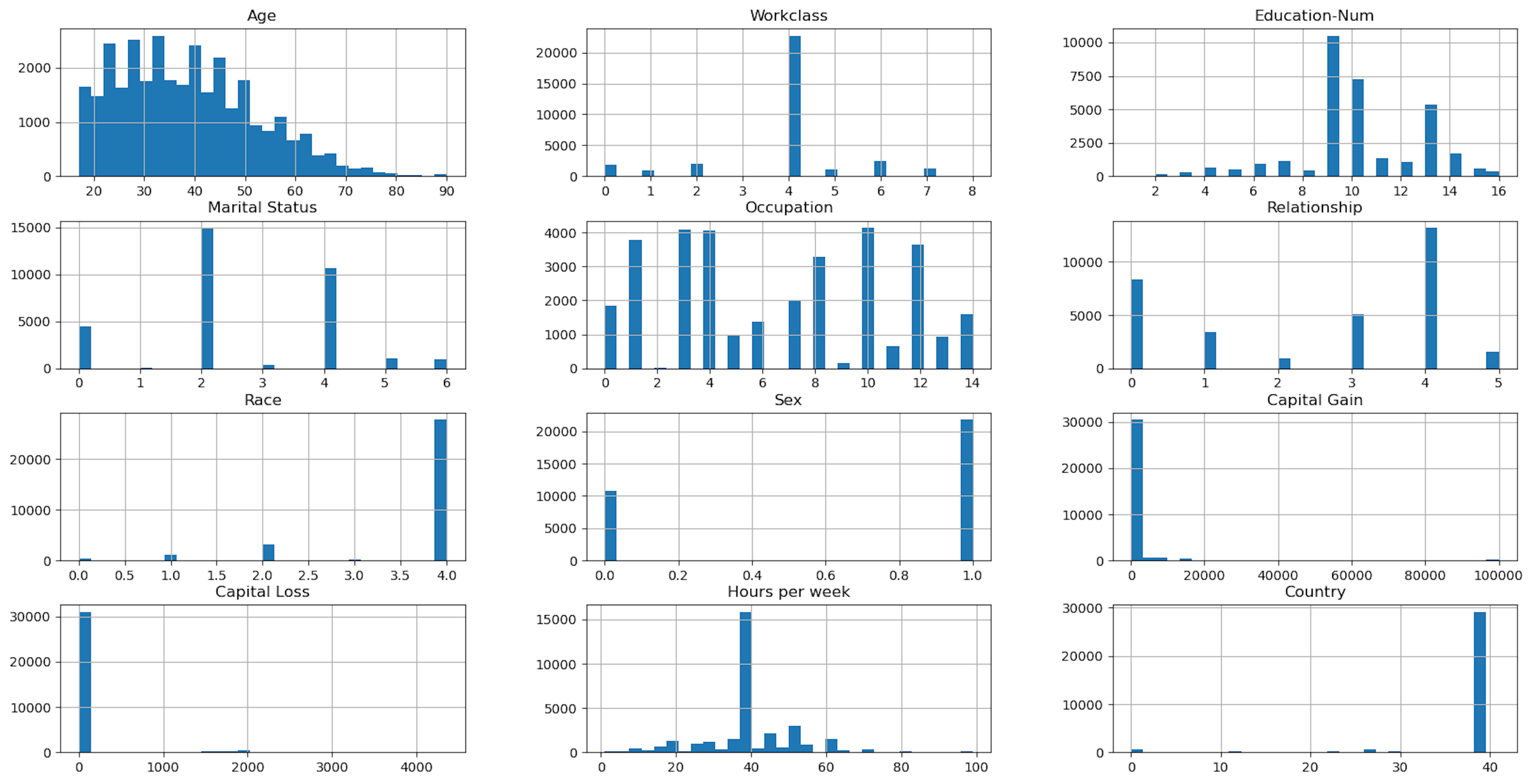
Important Note
- Choosing an appropriate number of bins is important in creating a meaningful and informative histogram.
- Too few bins may oversimplify the distribution, while too many bins may introduce noise and make it harder to identify patterns.
- The choice of bin size can impact the visual representation of the data, so it's often a good idea to experiment with different bin sizes to find the one that best reveals the underlying distribution.
What is sharey or sharex In Histogram?
- Specifies whether the y-axis or x-axis should be shared among histogram.
- When set to True, it means that all histograms will share the same y-axis or x-axis, making it easier to compare the distributions across different features.
- In our case, sharey=True will make our histogram more presentable, as main goal with histogram is correct and presentable representation of the distribution of data
hist = X.hist(figsize=(20, 10), bins=30, sharey=True)
Output: